Indian Council of World Affairs
Sapru House, New DelhiContextualising Arunachal Pradesh in India’s Development and Security Framework
Abstract: The geostrategic and geopolitical importance of Arunachal Pradesh is immense for India. This article attempts to understand and contextualise Arunachal Pradesh in India’s development and security framework.
Introduction
Arunachal Pradesh is India's strategic focal point. It is bordered by China, Myanmar, and Bhutan and has played an important role in shaping India’s foreign policy. However, territorial issues concerning Arunachal Pradesh have always created friction between India and China.
China’s strategic steps to affirm Arunachal Pradesh
China has often claimed parts of Arunachal Pradesh. The official Chinese map refers to Arunachal Pradesh as “Zangnan” or “South Tibet.” Initially, in 2017, the Chinese map standardised six places in the region, followed by 15 in 2021, another 11 more places in 2023 and recently added 30 more in 2024.[i]
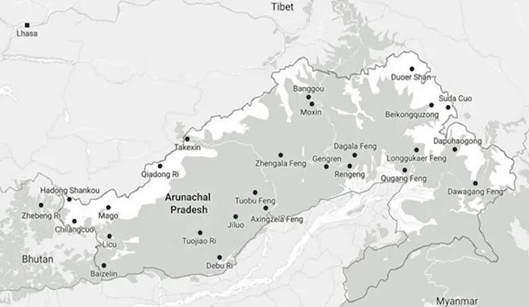
(Map of Arunachal Pradesh with names of cities as given by China)
Source: Eurasia Review[ii]
Since 2009, China has issued the “Stapled Visa Policy” for the people of the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh, and it continues to do so to date, to draw a distinction between the Indian citizens of Arunachal Pradesh and the rest of the Indian Population; a position unexpected to India. Often, the athletes from the region representing India and visiting China for international events have encountered problems due to this policy. Hence, many of them cannot participate in the events.[iii]
China is doing massive construction in the border areas adjoining Arunachal Pradesh. In November 2020, satellite images were captured indicating the presence of the newly constructed Chinese village consisting of 101 homes and around 4.5 km near the banks of the Tsari Chu River in the Upper Subansiri district of Arunachal Pradesh.[iv] Furthermore, in 2021 another satellite image was captured where 60 more buildings were built, which came 6 km inside the Shi Yomi district of the region.[v] The villages built by China in the border area violate the “Agreement between the Government of the Republic of India and the Government of the People’s Republic of China on the Political Parameters and Guiding Principles for the settlement of the India-China Boundary Question” of 2005. Article VII of the agreement states: “In reaching a boundary settlement, the two sides shall safeguard due interests of their settled populations in the border areas.”[vi]

(Growing presence of Chinese villages at the border : Satellite image)
Source – India Today NE. [vii]

(Growing presence of Chinese villages at the border : Satellite images)
Source – Times of India. [viii]
China continues extending its strategic presence along the border, such as enhancing the power supply for the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) positioned along the border, which is a top priority of its military-civilian fusion program. This power growth directly threatens India’s security because the PLA’s ability to monitor, move and deploy quickly along the Line of Actual Control gets better with a steady electricity supply. [ix]
China has always objected to any Indian high official's visit to the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The most recent bickering between the two sides regarding this matter happened in 2024 when Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited the region to inaugurate the Sela Tunnel in Tawang, about which the Chinese MFA spokesperson Wang Wenbin stated, “India’s relevant moves only complicate the boundary question and disrupt the situation in the border areas between the two countries.”[x] Subsequently, the Indian MEA spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal responded that “Indian leaders visit Arunachal Pradesh from time to time, as they visit other states of India. Objecting to such visits or India’s developmental projects does not stand to reason.”[xi]
Indian initiatives and development projects in Arunachal Pradesh
The Indian government, in response, has also taken its initiatives. It is a way of bolstering border security as well as ensuring regional development as a way of reaffirming that Arunachal Pradesh has always been and will continue to be part of Indian territory. India has taken several initiatives, such as the approval of the “Arunachal Frontier Highway,” a 1,637 km highway connecting 12 districts of the state along the Line of Actual Control, as a step to prevent China’s encroachment in the region as well as to develop the social economic growth in the region, with an estimated cost of 40,000 crore rupees.[xii] One more major project initiated by the Government of India is the planning of “12 hydroelectric power stations” in the region, with an investment of $1 billion, to which the finance minister has approved outlays for each hydropower project in the region.[xiii]
Additionally, a significant amount of development projects have been introduced in the region by the Indian government, such as the Donyi Polo Airport as the first greenfield project at the cost of more than 640 crore rupees.[xiv] Yet another major development project introduced in the region is the inauguration of the “Sela Tunnel,” the world’s longest bi-lane tunnel exceeding 13,000 feet, connecting Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh and Tezpur in Assam, successfully executed by the Border Road Organization (BRO), at the cost of 825 crore rupees.[xv]
In conclusion, India must keep strengthening its energy and defence capabilities in Arunachal Pradesh while keeping a careful eye on China’s course. It is important to continue the developmental projects in Arunachal Pradesh so that they are directly connected to the other states of India, while also accommodating the unique concerns and issues of the state to effectively tackle these challenges.
*****
*Bengia Mero, Research Intern, Indian Council of World Affairs, New Delhi
Disclaimer: Views expressed are personal.
Endnotes
[i] Tenzin Pema, China renames 30 Places In Indian-controlled Arunachal Pradesh, Eurasia Review, April 04, 2024, https://www.eurasiareview.com/03042024-china-renames-30-places-in-indian-controlled-arunachal-pradesh/
, accessed on January 21, 2025.
[ii] Tenzin Pema, China renames 30 places in India-controlled Arunachal Pradesh, Eurasia Review, April 04, 2024, https://www.eurasiareview.com/03042024-china-renames-30-places-in-indian-controlled-arunachal-pradesh/ , accessed on January 21, 2025.
[iii] Sounak Mukhopadhyay, Explained: China issuing ‘stapled visas’ to Arunachal Pradesh players may concern national security; here’s how, livemint, July 28, 2023, https://www-livemint-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/www.livemint.com/news/india/explained-china-issuing-stapled-visas-to-arunachal-pradesh-players-may-concern-national-security-heres-how/amp-11690521087136.html?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17383118053339&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&am=&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.livemint.com%2Fnews%2Findia%2Fexplained-china-issuing-stapled-visas-to-arunachal-pradesh-players-may-concern-national-security-heres-how-11690521087136.html , accessed on January 22, 2025.
[iv] Vishnu Som, Exclusive: China Has Built Village In Arunachal, Show Satellite Images, NDTV, January 18, 2021, https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/china-has-built-village-in-arunachal-pradesh-show-satellite-images-exclusive-2354154, accessed on January 21, 2025.
[v] Second Chinese village along Arunachal border: Satellite images, The Times of India, November 19, 2021, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/second-chinese-village-alongarunachal-border-sat-images/amp_articleshow/87788526.cms, accessed on January 23, 2025.
[vi] Agreement between the Government of the Republic of India and the Government of the People's Republic of China on the Political Parameters and Guiding Principles for the Settlement of the India-China Boundary Question, MEA, April 11,2005, https://www.mea.gov.in/bilateral-documents.htm?dtl/6534/Agreement+between+the+Government+of+the+Republic+of+India+and+the+Government+of+the+Peoples+Republic+of+China+on+the+Political+Parameters+and+Guiding+Principles+for+the+Settlement+of+the+IndiaChina+Boundary+Question, accessed on February 1, 2025.
[vii] India Today NE, January 19, 2021. https://www.indiatodayne.in/arunachal-pradesh/story/china-has-built-village-arunachal-pradesh-reports-400732-2021-01-19, accessed on January 24, 2025
[viii] Times of India, November 19, 2021, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/second-chinese-village-along-arunachal-border-sat-images/articleshow/87788526.cms, accessed on January 24, 2025.
[ix] Fan Chen, PLA extends power supply to border outposts near disputed China-India frontier, South China Monitor Post, January 29, 2025, https://amp-scmp-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/amp.scmp.com/news/china/military/article/3296615/pla-extends-power-supply-border-outposts-near-disputed-china-india-frontier?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17385622484559&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&am=&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.scmp.com%2Fnews%2Fchina%2Fmilitary%2Farticle%2F3296615%2Fpla-extends-power-supply-border-outposts-near-disputed-china-india-frontier, accessed on January 30, 2025.
[x] China lashes out at PM’s visit to Arunachal Pradesh, criticises Sela Tunnel and development projects, The Hindu, March 11, 2024, https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/china-lodgesdiplomatic-protest-over-pm-modis-visit-to-arunachal-pradesh/article67938502.ece/amp/, accessed on January 26, 2025
[xi] India rejects China’s comments on PM Modi’s visit to Arunachal Pradesh: ‘It will not change the
reality’, Hindustan Times, March 12, 2024, https://www-hindustantimes-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-rejects-chinas-comments-on-pm-modis-visit-to-arunachal-pradesh-101710220837704-amp.html?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17388267412552&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.hindustantimes.com%2Findia-news%2Findia-rejects-chinas-comments-on-pm-modis-visit-to-arunachal-pradesh-101710220837704.html, accessed on January 26, 2025.
[xii] Centre Approves Rs 28,229 Crore For 1,637 Km Arunachal Frontier Highway Along LAC, NDTV, November 28, 2024, https://www-ndtv-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/www.ndtv.com/india-news/centre-approves-rs-28-229-crore-for-1-637-km-arunachal-highway-along-lac-7121910/amp/1?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_ct=1738220101416&_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17382194205998&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ndtv.com%2Findia-news%2Fcentre-approves-rs-28-229-crore-for-1-637-km-arunachal-highway-along-lac-7121910, accessed on January 25, 2025.
[xiii] India races to build power plants in region claimed by China, The Economic Times, July 09, 2024, https://m-economictimes-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/m.economictimes.com/industry/energy/power/india-races-to-build-power-plants-in-region-claimed-by-china-sources-say/amp_articleshow/111608764.cms?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17382205701370&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&=&share=https%3A%2F%2Fm.economictimes.com%2Findustry%2Fenergy%2Fpower%2Findia-races-to-build-power-plants-in-region-claimed-by-china-sources-say%2Farticleshow%2F111608764.cms, accessed on January 25, 2025.
[xiv] All-weather licence granted to Donyi Polo airport in Itanagar; night landing soon, The Hindu,
[xv] 5 Facts About Sela Tunnel, World’s Longest Bi-Lane Project In Arunachal, NDTV, March 09, 2024, https://www-ndtv-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/www.ndtv.com/india-news/5-facts-about-the-worlds-longest-bi-lane-sela-tunnel-set-to-be-inaugurated-by-pm-modi-5204917/amp/1?amp_gsa=1&_js_v=a9&usqp=mq331AQIUAKwASCAAgM%3D#amp_tf=From%20%251%24s&aoh=17382215539208&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&share=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ndtv.com%2Findia-news%2F5-facts-about-the-worlds-longest-bi-lane-sela-tunnel-set-to-be-inaugurated-by-pm-modi-5204917, accessed on January 26, 2025.